آقاي ساسان سلام
اگر بيماري در حال پيشرفت باشد،نقاط جديد بدن كه تازه دارند رنگدانه از دست مي دهند ولي هنوز روند پيشرفت ادامه دارد،خيلي سفيد نيستند،در خصوص سوال دوم،چنين آمپول و درماني وجود ندارد،بهترين درمان براي شما نور درماني هست .
- Electrosurgery refers to the use of electricity to cause thermal tissue destruction, most commonly in the form of tissue dehydration, coagulation, or vaporization.- Electrosurgical procedures may be divided into four types based on their mechanism of tissue damage
- Uses direct current to induce tissue damage via a chemical reaction at the electrode tip.
- Uses high-frequency alternating current to ionize an electrically conductive medium (usually isotonic saline solution) and transmits heat to cause superficial epidermal and dermal damage with minimal collateral tissue destruction. - Coblation is used for facial rejuvenation.
- Uses tissue resistance to the passage of high-frequency alternating current to convert electric energy to heat, resulting in thermal tissue damage. - Heat generation occurs within the tissue, while the treatment electrode remains 'cold.' - This method includes electrodesiccation, electrofulguration, electrocoagulation, and electrosection. Electrosurgical procedures may be classified based on the degree of tissue destruction: - Superficial: electrodesiccation and electro fulguration - Deep: electrocoagulation - Tissue cutting: electrosection
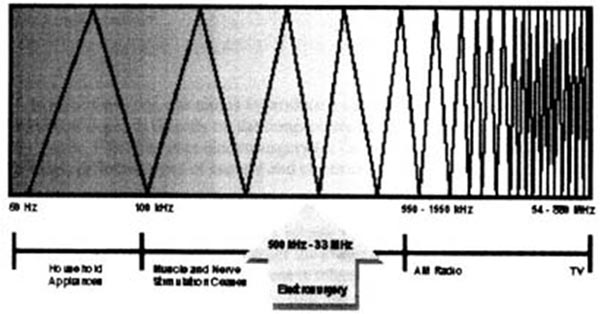
An electrosurgical unit is essentially a high-frequency current generator consisting of three components:
(1) a transformer that modifies the voltage,
(2) an oscillating circuit that increases the frequency, and
(3) the patient circuit that is comprised of the handpiece, the patient, and, in certain cases, the indifferent electrode 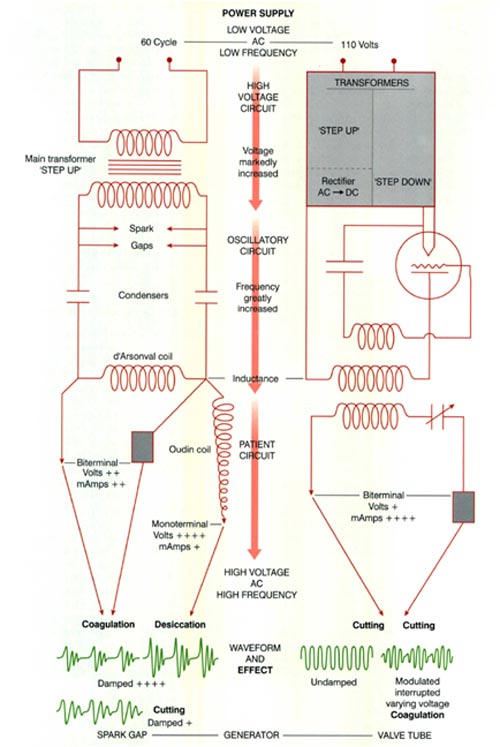
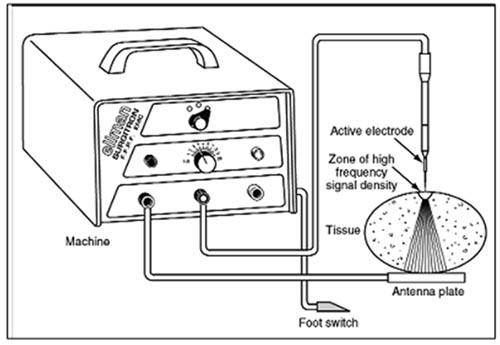
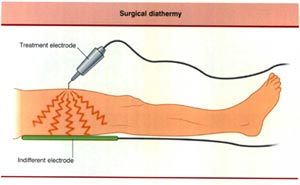
Decreasing the surface area of the treatment electrode increases current density.
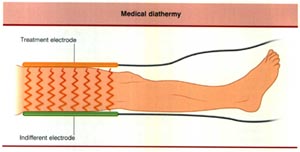
Increasing the surface area of the treatment electrode decreases current density.
If the tissue is heated very slowly the following events occur:
- Below 45 degree C — The thermal damage is reversible.
- Above 45 degree C — The cell enzymes are denatured and tissue necrosis starts.
- 70 degree C — The protein contents lose their quaternary configuration and solidify. This is seen as blanching of tissue. We call this as coagulation.
- 90 degree C — The liquid contents evaporate until tissue is completely dry — desiccation. This is seen as shrinkage.
- 200 degree C — Carbonisation starts. It refers to the end product of further heating of desiccated tissue. The solid contents of the tissue are reduced to carbon.
- When the tissue temperature is increased instantaneously from 37 to 100 degrees C, the above steps are short-circuited.
- The liquid contents of the cell are converted into vapour (steam) and the cell explodes producing a cutting effect.
 Unipolar System
Unipolar System 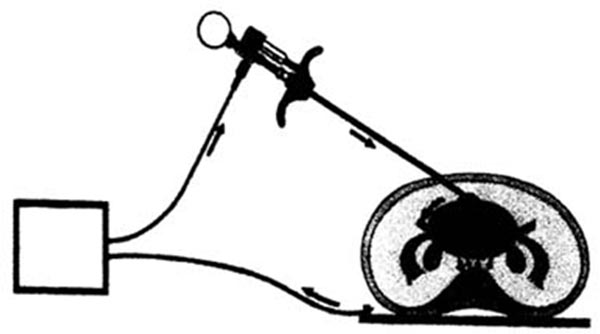 Bipolar System
Bipolar System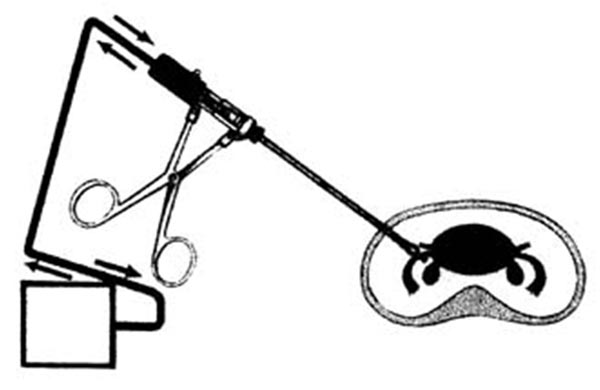
The only difference between the "active" electrode and the "patient-return" electrode is their relative size and conductivity. - Concentrate the electrons at the active electrode and high heat is produced.
- Disperse this same current over a comparatively large patient return electrode and little heat is produced.
- The pad should present a large, low impedance contact area to the patient. Placement should be on conductive tissue that is close to the operative site. Patient Return Electrodes
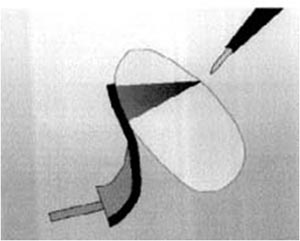
Return plate is not properly placed. If the current flow is high, it may produce burns on the skin. 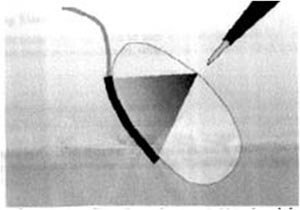 Properly placed return plate. Since the surface area is high, there is low current density.
Properly placed return plate. Since the surface area is high, there is low current density.
Choose a well-vascularised muscle mass close to the operating area. - Avoid less vascular areas, hairy areas, irregular body contours and bony prominence.

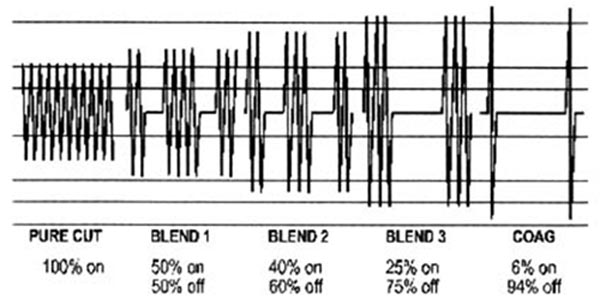
- Waveform- Power setting
- Size of the electrode - Time - Manipulation of the electrode - Type of tissue - Eschar 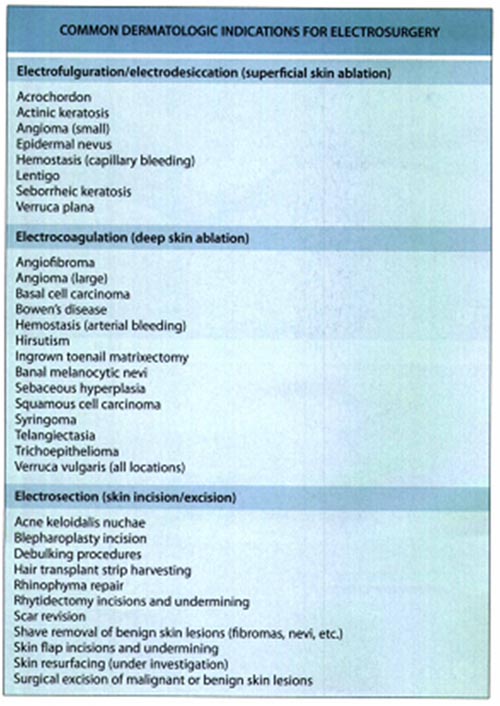
آقاي ساسان سلام
اگر بيماري در حال پيشرفت باشد،نقاط جديد بدن كه تازه دارند رنگدانه از دست مي دهند ولي هنوز روند پيشرفت ادامه دارد،خيلي سفيد نيستند،در خصوص سوال دوم،چنين آمپول و درماني وجود ندارد،بهترين درمان براي شما نور درماني هست .
زمان بهترین و ارزشمندترین هدیه ای است كه می توان به كسی ارزانی داشت.هنگامی كه برای كسی وقت می گذاریم، قسمتی از زندگی خود را به او میدهیم كه باز پس گرفته نمی شود . باعث خوشحالی و افتخار من است كه برای عزیزی مثل شما وقت می گذارم و امیدوارم كه با راهنماییهای اساتید این رشته واظهار نظر شما عزیزان این سایت آموزشی پر بارتر گردد.