آقاي ساسان سلام
اگر بيماري در حال پيشرفت باشد،نقاط جديد بدن كه تازه دارند رنگدانه از دست مي دهند ولي هنوز روند پيشرفت ادامه دارد،خيلي سفيد نيستند،در خصوص سوال دوم،چنين آمپول و درماني وجود ندارد،بهترين درمان براي شما نور درماني هست .
Archives of Dermatologic Research Immunoadsorption in Dermatology
Enno Schmid
Introduction
The arrival of immunoadsorption (IA), also termed immunoapheresis, about 20 years ago [25] allowed the selective removal of Ig and immune complexes from patients’ circulation.
IA has been successfully used in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, multiple sclerosis, dilated cardiomyopathy, antibody-mediated graft rejection, Guillain–Barré syndrome, ABO-incompatible kidney transplantation, rheumatoid arthritis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, and hemophilia with inhibitors In the latter three disorders, IA has been approved by the US American Food and Drug Administration. IA depletes Ig irrespective of its Specifcity. Specifc adsorbers have been developed for autoantibodies to the 1-adrenergic receptor in dilated cardiomyopathy (CoraYn®, Fresenius Medical Care), C1q in systemic lupus erythematosus (Miro®, Fresenius Medical Care), and to ABO blood group antigens .
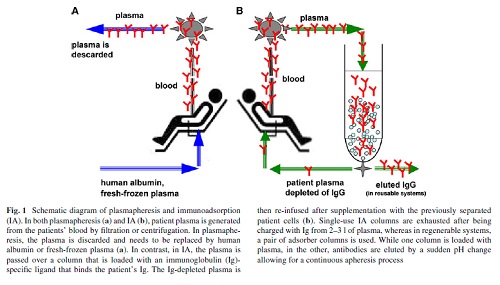
When compared with plasmapheresis, IA has several advantages: IA (1) more selectively removes Ig, (2) does not require the substitution of plasma components such as fresh-frozen plasma or human albumin (Fig. 1), (3) allows the processing of the two- to threefold plasma volume per treatment session, and (4) it is associated with a lower rate of adverse events, such as infections and allergic reactions Immunoadsorption systems differ with respect to ligands, matrix, volume of the columns, affinity to certain Ig classes and reusability. As an adsorber matrix, usually, sepharose is used, but cellulose and polyvinyl alcohol is also applied(Table 1).
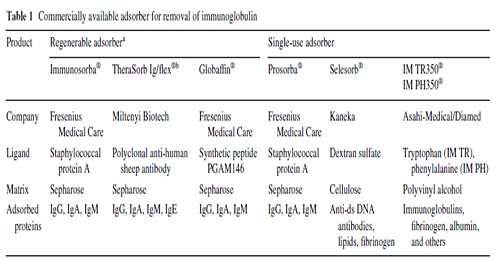
In single-use devices, phenylalanine, tryptophan, dextran sulfate, and hydrophobic amino acids serve as ligands. Adsorbers capable of being regenerated contain the ligands protein A, the synthetic peptide PGAM146, or sheep antibodies-directed against human Ig (Table 1).
No differences in IgG depletion rates between the protein A-based and the anti-human Ig-based reusable systems have been observed [38].
In the first step of IA, plasma and cellular components are separated by plasma Wltration or centrifugation (Fig. 1). Single-use adsorbers are subjected to the patient plasma until their capacity is utilized. In reusable systems, a pair of adsorber columns is used.
Current protocol
Based on these data, the strength of IA in pemphigus seemed to rely on the rapid induction of clinical remission by swift reduction of circulation autoantibodies during the first weeks of treatment rather then the infuence of longterm outcome.
To maximize this effect, we currently perform IA on three consecutive days (referred to as 1 cycle) followed by additional cycles 3 weeks later and then 4 weekly until lesions have healed for 90% and serum autoantibodies have dropped to 10% of original levels (Fig. 3).
Rituximab is applied twice at a dose of 1 g on days 4 and 25. This schedule was based on the one for rheumatoid arthritis for which rituximab had meanwhile been licensed.
Unlike the rituximab protocol for rheumatoid arthritis in pemphigus, the second IA cycle and the second rituximab infusion were performed 3 weeks after the initial infusion to avoid reducing rituximab levels by subsequent IA.
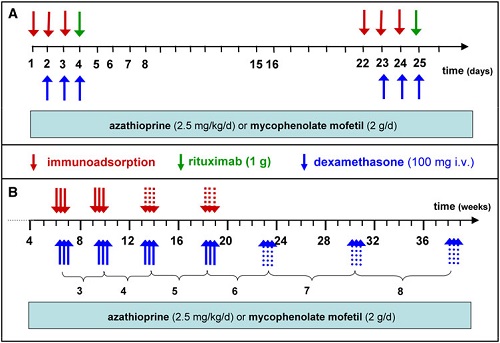

To decrease the rate of severe side effects encountered in Protocol 5 (see below), oral prednisolone was replaced by i.v. dexamethasone pulses (100 mg on 3 consecutive days) applied in conjunction with each IA. As in previous protocols, azathioprine or mycophenolate are also given (Fig. 3).
Until now, 15 patients have been subjected to this protocol.
Rapid clinical responses were seen (Fig. 4) while only two severe adverse events have occurred .
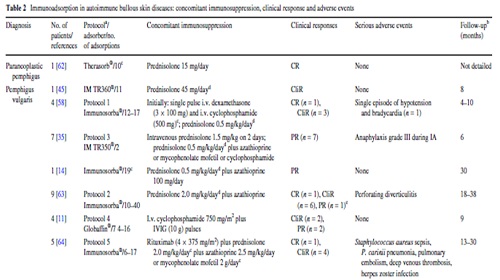
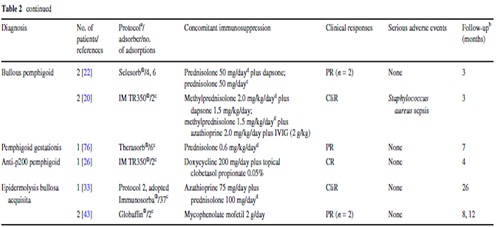
IA treatment of three additional patients with refractory pemphigus vulgaris has been reported . Among them, one patient received monthly IA for almost 2 years. Further details are presented in Table 2.
Adverse events
Of all adverse events, only four appear to be directly related to IA: a single episode of hypotension and bradycardia as well as a grade III anaphylactic reaction during the IA procedure and Staphylococcus aureus sepsis after infection of the central venous catheter in two patients (Table 2).
The relatively low incidence of adverse events seen in autoimmune blistering diseases is in line with data from the Swedish Apheresis Group that reported adverse events in <1% of procedures.


Recommendations
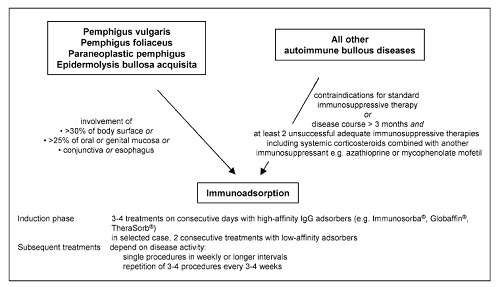
Below, recommendations for the use of IA in the treatment of autoimmune bullous diseases that have been published following a consensus meeting of German, Austrian, and Swiss physicians experienced in IA are summarized
(Contra-) indications
Immunoadsorption may be performed as first-line treatment in pemphigus or epidermolysis bullosa acquisita patients with acute and severe disease [defined as involvement of
(1) >30% of the body surface or
(2) >25% of oral or genital mucous membranes or
(3) conjunctiva or
(4) esophagus].
In patients with other autoimmune blistering disorders, IA should be reserved for refractory patients with disease courses of more than 3 months and at least two adequate immunosuppressive therapies (Fig. 5).
Contraindications
IA may not be performed in patients with known hypersensitivity to column material, severe cardiovascular disease, extreme bleeding tendency during anticoagulation, treatment with ACE inhibitors (discontinue drugs at least 72 h before IA), and children under 15 kg of body weight.
Perspectives
Regarding all available data, IA appears to be a rational, effective, and relatively safe adjuvant therapy for severe and/or treatment-resistant autoimmune bullous disorders.
IA allows the rapid reduction of serum autoantibodies which is reflected by rapid clinical responses.
In our experience, the rapid clinical effect following IA obtained in most of these patientsis,for the time being,ideally complemented with rituximab
آقاي ساسان سلام
اگر بيماري در حال پيشرفت باشد،نقاط جديد بدن كه تازه دارند رنگدانه از دست مي دهند ولي هنوز روند پيشرفت ادامه دارد،خيلي سفيد نيستند،در خصوص سوال دوم،چنين آمپول و درماني وجود ندارد،بهترين درمان براي شما نور درماني هست .
زمان بهترین و ارزشمندترین هدیه ای است كه می توان به كسی ارزانی داشت.هنگامی كه برای كسی وقت می گذاریم، قسمتی از زندگی خود را به او میدهیم كه باز پس گرفته نمی شود . باعث خوشحالی و افتخار من است كه برای عزیزی مثل شما وقت می گذارم و امیدوارم كه با راهنماییهای اساتید این رشته واظهار نظر شما عزیزان این سایت آموزشی پر بارتر گردد.